best test for supraspinatus tear|empty can exercise for shoulder : warehouse Supraspinatus Test The supraspinatus tendon is the most frequently injured tendon of the rotator cuff. To test for integrity of the supraspinatus we can ask the patient to abduct both arms to 90° and then to bring them anteriorly with a 30° forward flexion.
Yes, polypropylene is autoclavable. It can withstand the high temperature and pressure conditions of an autoclave, which makes it suitable for sterilization purposes.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Poteau bois 12x12 : la sélection produits Leroy Merlin de ce vendredi au meilleur prix ! Retrouvez ci-après nos 41 offres, marques, références et promotions en stock prêtes à être livrées .
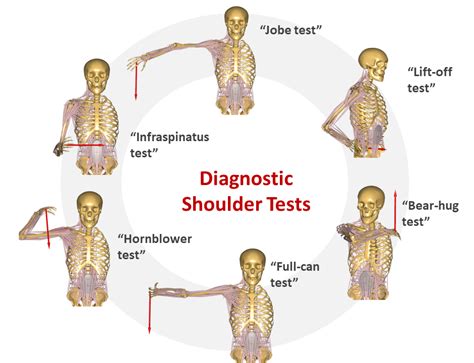
Below are 5 easy Physical Therapy tests you can use to identify whether your rotator cuff is compromised or torn. If have someone else at home capable of following simple directions, ask them to help you by applying oppositional force. Otherwise, if you’re home alone, no worries – you can just use . See moreSo to review, I recommend the following tests for a rotator cuff tear: 1. Empty Can Test 2. Drop Arm Test 3. Lag Sign 4. Infraspinatus Test 5. Lift-Off Test If you . See morePhysical Therapists conduct special tests as part of their overall assessment. Before provoking symptoms with orthopedic tests, your PT will gather as much . See more
Supraspinatus Test The supraspinatus tendon is the most frequently injured tendon of the rotator cuff. To test for integrity of the supraspinatus we can ask the patient to abduct both arms to 90° and then to bring them anteriorly with a 30° .
This test targets one of the rotator cuff muscles that most commonly tears at the tendon: the supraspinatus. To perform the empty can test, fully extend your bad arm and raise it to shoulder height, slightly outward from your body.Supraspinatus Test The supraspinatus tendon is the most frequently injured tendon of the rotator cuff. To test for integrity of the supraspinatus we can ask the patient to abduct both arms to 90° and then to bring them anteriorly with a 30° forward flexion. Patients were assessed with the most commonly used clinical shoulder tests, including the Jobe test (empty can), Neer test, drop arm test, Hawkins test, and full can test to identify supraspinatus tears and tendinosis.
Special testing is generally performed following a full examination of the shoulder that includes but is not limited to patient history, mechanism of injury, clinical observation, bony and soft tissue palpation, assessment of active and passive physiological movements, assessment of passive arthokinematic / accessory joint mobility, neurological.Clinical Relevant Anatomy. The shoulder joint is made up of three bones: the humerus, scapula and clavicle. The head of the humerus and the glenoid of the scapula form a ball-and-socket joint [1]. The supraspinatus muscle is located on the back of . Symptoms of a supraspinatus tear include: Sharp pain in the shoulder at the time of injury. Pain when the arm is rotated outwards and upwards. Increased pain and weakness when the arm is raised sideways between a 60-degree arc. Read more on how to . A positive lag sign with external rotation is the best test for full-thickness tears of the infraspinatus and supraspinatus (positive likelihood ratio = 7.2). A positive lag sign with.
The drop arm test is used to assess for full thickness rotator cuff tears, particularly of the supraspinatus. This can be useful when diagnosing sub-acromial pain syndrome (shoulder impingment) or to differentiate between shoulder and rotator cuff pathologies. The drop arm test may be more accurate when used in a battery of tests such as:
shoulder tests for rotator cuff
Supraspinatus test (full-can test). Apply downward force with the arm in 90° scaption and in external rotation (thumb up). If there is a supraspinatus tear, the patient cannot resist this force and the arm will be depressedMuscle weakness showed the best diagnostic precision compared with pain or using both criteria. No single clinical test was found to be useful to distinguish between partial- and full-thickness tears. A combination of at least 3 or more tests improved the diagnostic value.
describe autoclaving process
This test targets one of the rotator cuff muscles that most commonly tears at the tendon: the supraspinatus. To perform the empty can test, fully extend your bad arm and raise it to shoulder height, slightly outward from your body.Supraspinatus Test The supraspinatus tendon is the most frequently injured tendon of the rotator cuff. To test for integrity of the supraspinatus we can ask the patient to abduct both arms to 90° and then to bring them anteriorly with a 30° forward flexion. Patients were assessed with the most commonly used clinical shoulder tests, including the Jobe test (empty can), Neer test, drop arm test, Hawkins test, and full can test to identify supraspinatus tears and tendinosis.
Special testing is generally performed following a full examination of the shoulder that includes but is not limited to patient history, mechanism of injury, clinical observation, bony and soft tissue palpation, assessment of active and passive physiological movements, assessment of passive arthokinematic / accessory joint mobility, neurological.Clinical Relevant Anatomy. The shoulder joint is made up of three bones: the humerus, scapula and clavicle. The head of the humerus and the glenoid of the scapula form a ball-and-socket joint [1]. The supraspinatus muscle is located on the back of . Symptoms of a supraspinatus tear include: Sharp pain in the shoulder at the time of injury. Pain when the arm is rotated outwards and upwards. Increased pain and weakness when the arm is raised sideways between a 60-degree arc. Read more on how to .
shoulder special tests rotator cuff
A positive lag sign with external rotation is the best test for full-thickness tears of the infraspinatus and supraspinatus (positive likelihood ratio = 7.2). A positive lag sign with.The drop arm test is used to assess for full thickness rotator cuff tears, particularly of the supraspinatus. This can be useful when diagnosing sub-acromial pain syndrome (shoulder impingment) or to differentiate between shoulder and rotator cuff pathologies. The drop arm test may be more accurate when used in a battery of tests such as:
Supraspinatus test (full-can test). Apply downward force with the arm in 90° scaption and in external rotation (thumb up). If there is a supraspinatus tear, the patient cannot resist this force and the arm will be depressed
rotator cuff tear physical exam


describe the use of an autoclave in microbiology laboratory
describe why chemical sterilization might be used instead of autoclaving.
This method requires the use of an autoclave. To sterilize, temperature must reach 121°C for a minimum of 15 minutes.
best test for supraspinatus tear|empty can exercise for shoulder